In the past decade, artificial intelligence (AI) has shifted from a futuristic concept to a cornerstone of modern business. AI’s impact is segmented into two sectors: AI in supply chain and AI in financial technology (fintech). Manual processes, slow decision cycles, and fragmented data once defined these industries.
Today, intelligent algorithms are reshaping how goods move across the globe, how money flows, and how decisions are made, faster, brighter, and more reliably than ever before.

AI in Supply Chain
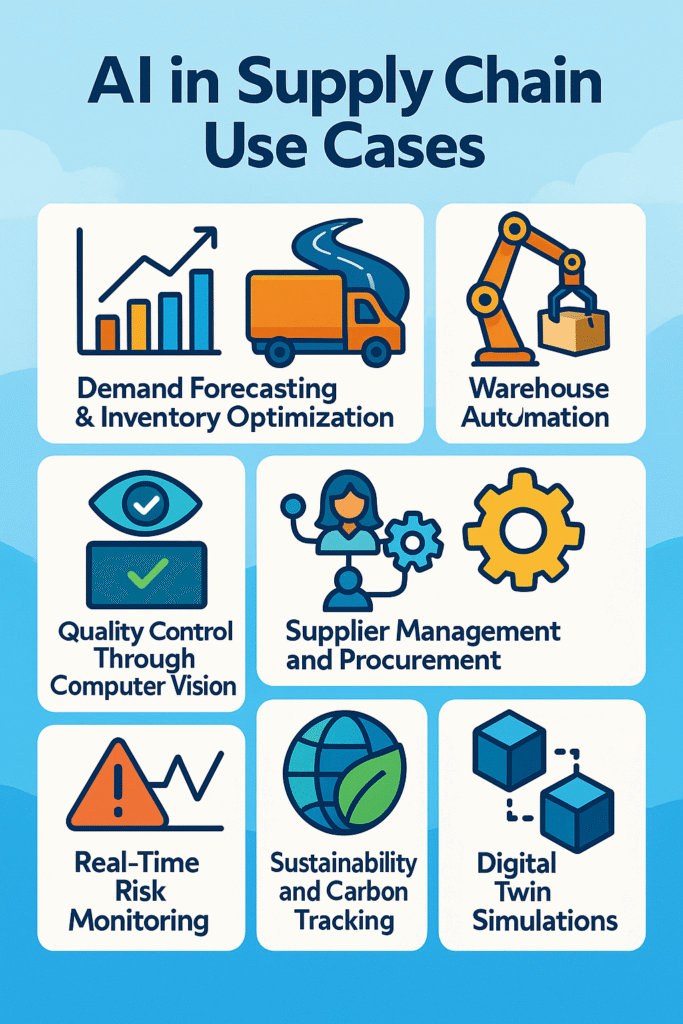
AI in the supply chain can be used in several ways.
1. Demand Forecasting & Inventory Optimization
Forecasting forms the nucleus of any supply chain and involves projecting what customers will buy, when, and where. Retail giants like Walmart and Target utilize AI in their supply chain models to analyze historical sales data, local weather patterns, regional trends, and social signals, generating highly reliable predictions. Such systems might, for example, track the sudden surge in sweater demand in New England as a cold snap approaches or charcoal sales increase near barbecue spots on a hot weekend.
Results such as these were realized:
AI in the supply chain delivered outstanding outputs like:
-
- Higher Inventory Availability: Target observed coverage of fast-moving items double over two years.
-
- Lower Waste and Overstock: Inventory lying in less-demanded items,
-
- Higher Customer Satisfaction: A lower number of out-of-stock situations.
And the payoffs, they are real! According to research, companies that utilize AI-based forecasting can reduce inventory costs by 20-30% and increase service levels by up to 65%.
2. Logistics and Route Optimization
Transporting goods across cities, countries, or continents involves countless variables—from driver schedules to customs brokering, traffic jams to fuel prices. AI systems process real-time and historical data to identify the most efficient routes, spot delivery delays, and dynamically re-route shipments. For example:
-
- Uber Freight uses AI to reduce “deadhead miles” (empty truck trips), saving carriers up to 15% in costs.
-
- UPS estimates improved route optimization can cut its annual fuel bill by millions, reducing CO₂ emissions at the same time.
This optimization isn’t limited to trucking. Sea freight, rail, even last-mile bike or drone delivery all benefit from intelligent planning, creating a leaner, greener transport network.
3. Warehouse Automation with Robotics
A greater array of robots is employed alongside humans in modern warehouses today. Fleet deployment of mobile robots examples include Amazon and Ocado: those robots pick, sort, and carry things, thereby freeing the human workforce from monotonous and laborious works.
These robots identify items, avoid obstacles, and recalibrate routes as warehouse layouts change through the use of AI. Thus, with the accomplishment of faster fulfillment, there are fewer chances of errors and an elevated capacity without the need for physical space expansion. Warehouse managers report productivity gains of 30-50% when using the system correctly and safely.
4. Quality Control Through Computer Vision
Packing and inspecting thousands of products manually is slow and often inconsistent. AI-powered computer vision cameras can evaluate goods in real time—spotting scratches, dents, leaks, or misprints far more accurately than the human eye. Major food and beverage companies, as well as electronics manufacturers, employ these systems to limit recalls and improve consumer trust.
Accuracy rates often exceed 95%, increasing quality consistency and reducing waste.
5. Supplier Management and Procurement
Sourcing of materials is not just a matter of determining price; it also involves considering supplier reliability, compliance, and geopolitical risk. AI tools, therefore, take into consideration supplier performance:
-
- Delivery on time or late, number of defects on quantity supplied, compliance flags, financial stability, and social responsibility scores.
-
- If certain signs of risk appear for a supplier, the AI system can trigger alerts and give precedence to sourcing from alternatives previously vetted.
-
- This kind of supervision enables companies to respond promptly to adverse events, resulting in reduced lead time, a fast response to market changes, and lower risk exposure.
6. Predictive Maintenance for Vehicles and Equipment
Breakdowns in transport fleets or warehouse machinery can cause delays and unnecessary costs. AI systems monitor vehicle and equipment sensor data—vibrations, temperature, oil quality—and detect warning signs before machines fail.
This “predictive maintenance” model helps companies:
-
- Schedule repairs when convenient.
-
- Avoid costly breakdowns,
-
- Extend equipment lifespan,
-
- Reduce maintenance costs by up to 40%.
7. Real-Time Risk Monitoring
International supply chains face constant threats—ports get congested, political unrest disrupts routes, or factories suffer cyberattacks. AI engines ingest news articles, social media posts, satellite images, and sensor data to provide early warning alerts for emerging risks.
For instance, if a hurricane is forecast near one port, the system might reroute shipments preemptively or shift production to another site, saving weeks of possible stoppages.
8. Sustainability and Carbon Tracking
With increasing pressure on businesses to reduce emissions, AI offers tools for meaningful ESG (environmental, social, governance) improvements. Through automated tracking of fuel consumption, route optimization, and equipment usage, AI calculates carbon footprints. It also supports reverse logistics—determining how and when to reuse or recycle returned products.
These insights inform sustainability dashboards and carbon reporting tools, enabling companies to meet targets and comply with regulatory or consumer demands.
9. Digital Twin Simulations
Digital twins are virtual versions of real-world supply chains. These models integrate data from inventory systems, transport logs, and external signals (like economics or weather). Executives can run “what-if” scenarios—such as detouring around a flooded region or reheating warehouse demand—and see the impact instantly.
This approach supports:
-
- Fast and confident decision-making,
-
- Planned responses to emergencies,
-
- Improved collaboration across global teams.
ROI and Impact in Supply Chain
Real-world data backs up AI’s impact:
-
- Inventory reduction: 20–30% fewer goods tied up in stock.
-
- Cost savings: Up to 15% lower logistics spending.
-
- Warehouse efficiency: 30–50% faster orders processed.
-
- Service quality: 35–65% more reliable deliveries.
Enterprises that embrace AI responsibly have transformed their operations, making them more agile, resilient, efficient, and transparent.
AI in Fintech
1. Credit Scoring and Inclusive Lending
Traditional credit scores exclude millions of individuals who lack a credit history. Enter fintechs like Upstart, Zest Finance, and Abound, which use AI to assess potential borrowers based on financial behaviors, job history, and even smartphone usage.
-
- Abound, a UK platform, grew revenue from £300K to £7.5M in less than a year by using AI underwriting—giving loans to underserved borrowers.
-
- AI has enabled banks to tap into new segments while effectively managing risk.
Approximately 70–80% of loan decisions in modern fintech incorporate AI models, significantly reducing decision times and mitigating human bias.
2. Fraud Detection and Anti-Money Laundering
Every transaction is a potential risk. AI systems analyze patterns in real time to flag unusual behavior:
-
- Multiple transactions from different countries minutes apart,
-
- Excessively large purchases inconsistent with a user’s history,
-
- Sudden fund flows in low-activity accounts.
Banks and online platforms experience significant decreases in fraud-related losses, while the number of false positives (legitimate transactions mistakenly blocked) also decreases, ensuring customer satisfaction and maintaining smooth operations.
3. Personalized Virtual Assistants
Fintech apps have intelligent chatbots and voice assistants operating 24/7 to serve the customers. They answer balance inquiries, help troubleshoot failed transactions, or support budgeting.
The conversation is delivered to human agents for complex issues. This is a positive experience for the user, reduces call center costs, and increases user satisfaction.
4. Algorithmic Trading and Risk Analytics
Hedge funds and large banks use AI engines to scan markets, run scenario simulations, allocate assets, and balance risk exposures in real time. Platforms like BlackRock’s Aladdin system allow portfolio managers to simulate millions of variables and design optimal investment mixes.
This translates into:
-
- Smarter portfolio decisions,
-
- Faster reactions to market swings,
-
- Better risk-adjusted returns.
5. Customer Churn and Retention Prediction
Fintechs utilize AI to identify users who may be on the verge of leaving. By analyzing login frequency, transaction patterns, or product adoption rates, models flag at-risk customers. Companies can then offer tailored incentives or outreach, improving retention and lifetime value.
6. Automated Compliance & Regulatory Reporting
According to various regulations (AML, KYC, PSD2, GDPR, CCPA), all businesses must perform several operations, which come with the additional burden of being both costly and time-consuming. Here is what AI can assist with:
-
- Automate record-keeping,
-
- Tag suspicious transactions,
-
- Prepare auditor or regulatory reports,
-
- Reduce fines by executing accurately and on time.
7. Smart Personal Finance Management
Apps like Cleo, Mint, and Walnut leverage AI to deliver personalized budgeting tips, spending forecasts, and savings goals. They analyze income flows and purchase behavior, then send reminders or recommend deals. According to reports, users of these apps save 10–20% more money annually than average consumers.
Fintech Market Trends & Statistics
-
- The AI in fintech market hit ~$13.5 billion in 2024, with projections nearing $60 billion by 2034—a 16–18% annual growth rate.
-
- 85% of large financial institutions report using AI in at least one core process; half consider AI a competitive necessity.
-
- Fintechs that integrate AI experience 3–15% gains in revenue performance, primarily due to reductions in fraud, improvements in customer service, and enhanced personalization.
Common Challenges & Solutions
Challenge 1: Data Quality and Integration
Why it matters: AI is only as good as its data. Many finance or logistics systems still rely on outdated, siloed databases.
Solution: Invest in robust data pipelines, maintain clean historical records, and establish clear data definitions.
Challenge 2: Interpretability & Trust
Why it matters: A “black-box” AI model might make accurate decisions, but without explanation, it raises compliance or ethical concerns.
Solution: Use “explainable AI” frameworks, show rule-based rationale with every decision, and retain human oversight.
Challenge 3: Regulation & Security
Why it matters: Financial data and cross-border logistics both involve sensitive information and compliance regimes.
Solution: Build systems by privacy standards (ISO 27001, PCI-DSS); regularly audit models; and collaborate with legal and compliance teams early on.
Challenge 4: Adoption & Culture
Why it matters: Even the best tools fail if employees don’t trust or understand them.
Solution: Run pilot programs, co-create with end users, and train teams to interpret and act on AI insights.
Future Trends in AI for Supply Chain & Fintech
| Trend | Description |
| Agentic AI | Systems that autonomously sense, decide, and act, like rerouting shipments or blocking suspicious transactions without prompting. |
| Generative AI & Digital Twins | Simulate scenarios, draft procurement requests, or even write policy summaries using AI — all in natural language. |
| Edge AI & IoT Networks | On-device intelligence in trucks, POS devices, and sensors—reducing latency and improving security. |
| Ethical AI and Regulation | “Trustworthy AI” frameworks will become the standard, featuring bias auditing, fairness metrics, and explainability reports. |
| Hyper-Personalization | Financial products tailored to life stages; logistics routes optimized according to customer priorities. |
| Climate-Conscious Supply Chains | Carbon tracking, eco-routing, and circular logistics are focused on sustainability compliance and brand responsibility. |
How to Start Your AI Journey
1. Define Business Objectives:
Understand the core problem (e.g., out-of-stocks, loan rejection) and estimate value improvement.
2. Audit Data and Systems:
Take an inventory of data sources, quality, and integration capability.
3. Pilot Small, Prove Fast:
Build minimally viable models to test impact—measure before-and-after.
4. Prioritize Ethics and Explainability:
Ensure AI recommendations can be understood, audited, and legally justified.
5. Upskill Your Teams:
Bring data scientists, engineers, and business users together—embed AI literacy.
6. Scale Systems, Not Pilots:
Once proven, invest in MLOps, security, and change management to roll solutions out.
Conclusion:
From artifice to prime technology in supply chain segregation and financial technology, AI is making logistics more innovative and more responsive. For instance, it enables real-time tracking of goods from the dock, optimizes routes, improves quality control, and reduces emissions. In finance, it underwrites loans, detects fraudulent activities, personalizes user experience, and manages portfolio risks. However, a mere touch of technology is insufficient.
Clear goals, solid foundations in data, ethical guardrails, and empowered teams will ensure success. If you are either refocusing an existing operation or venturing into a new business model, AI will double your effect-if you build it right.